Alpha Synuclein S87N Mutant Monomers
CAT:
400-SPR-499E
Size:
5x 100 µg
Price:
Ask
- Availability: 24/48H Stock Items & 2 to 6 Weeks non Stock Items.
- Dry Ice Shipment: Yes










Alpha Synuclein S87N Mutant Monomers
Background:
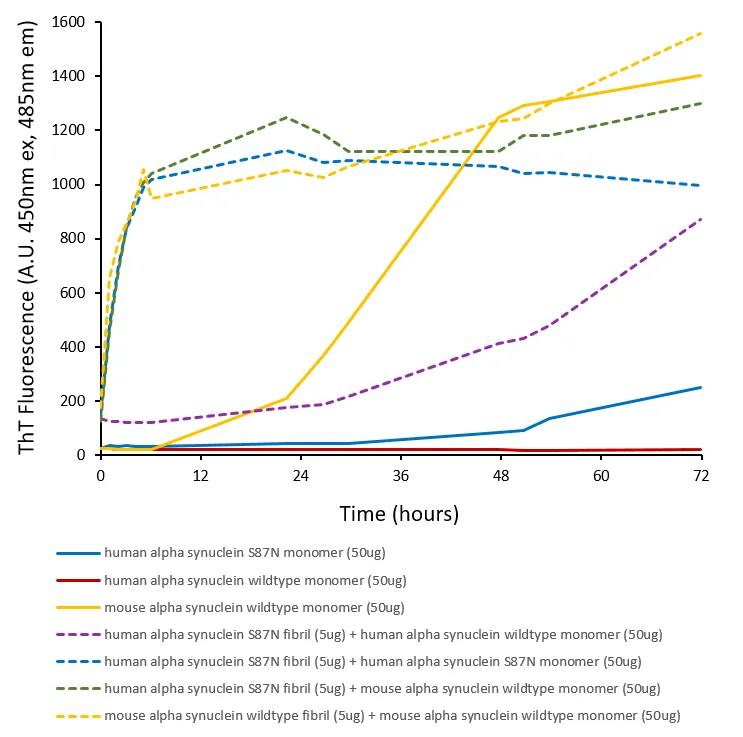
Human alpha synuclein S87N mutant (HuS87N) has Ser87 mutated to the equivalent mouse residue Asn87, effectively making it a human-mouse chimeric protein. Despite sequence differences at only seven residues, or 5% of the total 140 amino acids, the aggregation rate of wild-type mouse α-syn (MsWT) is faster than wild-type human α-syn (HuWT) in vitro. In wild-type mouse models, MsWT fibrils are more efficient than HuWT fibrils at inducing pathology of endogenous mouse α-syn (1). A53T or S87N substitutions in human α-syn substantially accelerate fibrilization rates in vitro (2,3). Chimeric HuS87N fibrils show enhanced pathogenicity to wild-type mouse neurons, greater than HuWT, HuA53T, and MsWT fibrils (4). HuS87N fibrils can be used as a more human-like alternative to MsWT fibrils to induce equivalent or greater endogenous α-syn seeding and pathology in wild-type mice.Description:
Human Recombinant Alpha Synuclein S87N Mutant MonomersProduct Name Alternative:
Alpha Synuclein S87N, Alpha synuclein protein, Alpha-synuclein protein, Non-A beta component of AD amyloid protein, Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor protein, NACP protein, SNCA protein, NACP protein, PARK1 protein, SYN protein, Parkinson's disease familial 1 ProteinUNSPSC:
12352202Gene ID:
6622Swiss Prot:
P37840-1Accession Number:
NP_000336.1Host:
E. coliOrigin Species:
HumanTarget:
Alpha Synuclein S87N MutantConjugation:
No TagSequence:
MDVFMKGLSKAKEGVVAAAEKTKQGVAEAAGKTKEGVLYVGSKTKEGVVHGVATVAEKTKEQVTNVGGAVVTGVTAVAQKTVEGAGNIAAATGFVKKDQLGKNEEGAPQEGILEDMPVDPDNEAYEMPSEEGYQDYEPEAApplications:
WB, SDS PAGE, In vitro AssayPurification Method:
Ion-exchange PurifiedConcentration:
2 mg/ml or 5 mg/mlPurity:
>95%Weight:
0.05Length:
140 AABuffer:
1X PBS pH 7.4Molecular Weight:
14.46 kDaPrecautions:
Not for use in humans. Not for use in diagnostics or therapeutics. For research use only.Additionnal Information:
For corresponding PFFs, see catalog# SPR-500References & Citations:
1. Masuda-Suzukake et al. 2013. Prion-like Spreading of Pathological α-synuclein in Brain. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/braiwt037 2. Kang, K. et al. 2011. The A53T Mutation is Key in Defining the Differences in the Aggregation Kinetics of Human and Mouse α-synuclein. JACS. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja203979j 3. Ohgita, T. et al. 2023. Intramolecular Interaction Kinetically Regulates Fibril Formation by Human and Mouse Alpha-Synuclein. Sci Rep https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-38070-4 4. Luk, K., C. et al. 2016. Molecular and Biological Compatibility with Host Alpha-Synuclein Influences Fibril Pathogenicity. Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.053
MSDS Document
View Document